Air Cooled Heat Exchanger
What is an Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger?
An air-cooled heat exchanger (ACHE) is a type of heat exchanger that uses ambient air to cool fluids or gases, effectively transferring heat from one medium to another. It is a highly effective solution for heat transfer in environments where water is scarce or unavailable. Air-cooled heat exchangers are used across a variety of industries, from power generation and HVAC systems to oil and gas, petrochemical, and manufacturing.
These exchangers help regulate temperature, optimize performance, and improve system efficiency by ensuring that fluids like oil, gas, and refrigerants stay within safe operating temperatures.
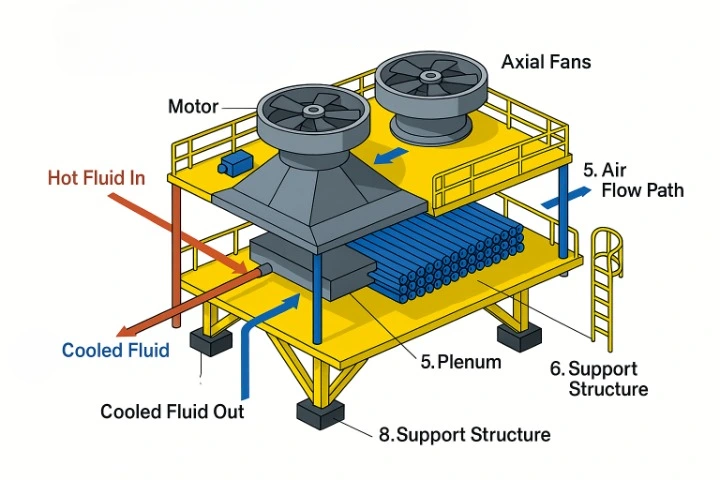
How Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers Enhance System Performance
1. Efficient Heat Transfer Using Ambient Air
Air-cooled heat exchangers utilize ambient air for heat dissipation, making them an energy-efficient solution for systems that require cooling without using water. They are designed with large surface areas and fins to maximize the exposure of the fluid to air, increasing heat exchange efficiency.
2. Space-Saving and Compact Design
Compared to traditional water-cooled exchangers, air-cooled models have a compact design, making them ideal for installations where space is limited. With no need for a separate water source or cooling tower, they offer a streamlined and easy-to-maintain solution.
3. Reduced Environmental Impact
By eliminating the need for water in the cooling process, air-cooled heat exchangers help reduce water consumption, making them environmentally friendly. This also minimizes the need for water treatment and wastewater management systems.
Types of Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
1. Fin-Fan Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger
The fin-fan air-cooled heat exchanger is one of the most commonly used types. It consists of a heat exchange coil with a series of fans that blow air across the coils, removing heat. These exchangers are ideal for applications that require high cooling capacity with minimal water usage.
2. Shell and Tube Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger
A shell and tube air-cooled heat exchanger uses a series of tubes (shell) through which the fluid flows. Outside the tubes, ambient air circulates to cool the fluid inside. This type is often used in larger industrial applications due to its ability to handle higher pressure and flow rates.
3. Indirect Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger
In an indirect air-cooled heat exchanger, the fluid being cooled does not directly contact the air. Instead, heat is transferred to a secondary cooling medium (like glycol or oil), which is then cooled by the ambient air. This design is often used in sensitive applications where direct exposure to air might not be ideal.
Applications of Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
1. Power Generation
In power plants, air-cooled heat exchangers play a critical role in cooling turbines, compressors, and other equipment, ensuring continuous and efficient operation without relying on a water supply.
2. HVAC Systems
For heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, air-cooled heat exchangers provide a reliable and efficient means of cooling refrigerants, helping maintain indoor climate control in both commercial and industrial buildings.
3. Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas industry, air-cooled heat exchangers are used to cool fluids during drilling, refining, and processing operations. They help manage the high temperatures generated in equipment such as compressors and pumps.
4. Petrochemical and Chemical Processing
In petrochemical plants, air-cooled heat exchangers are used to cool process fluids, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of reactors, distillation columns, and other equipment.
5. Manufacturing and Industrial Processes
From metalworking to food production, air-cooled heat exchangers are utilized in numerous industrial processes that require efficient cooling without the need for water-based cooling systems.
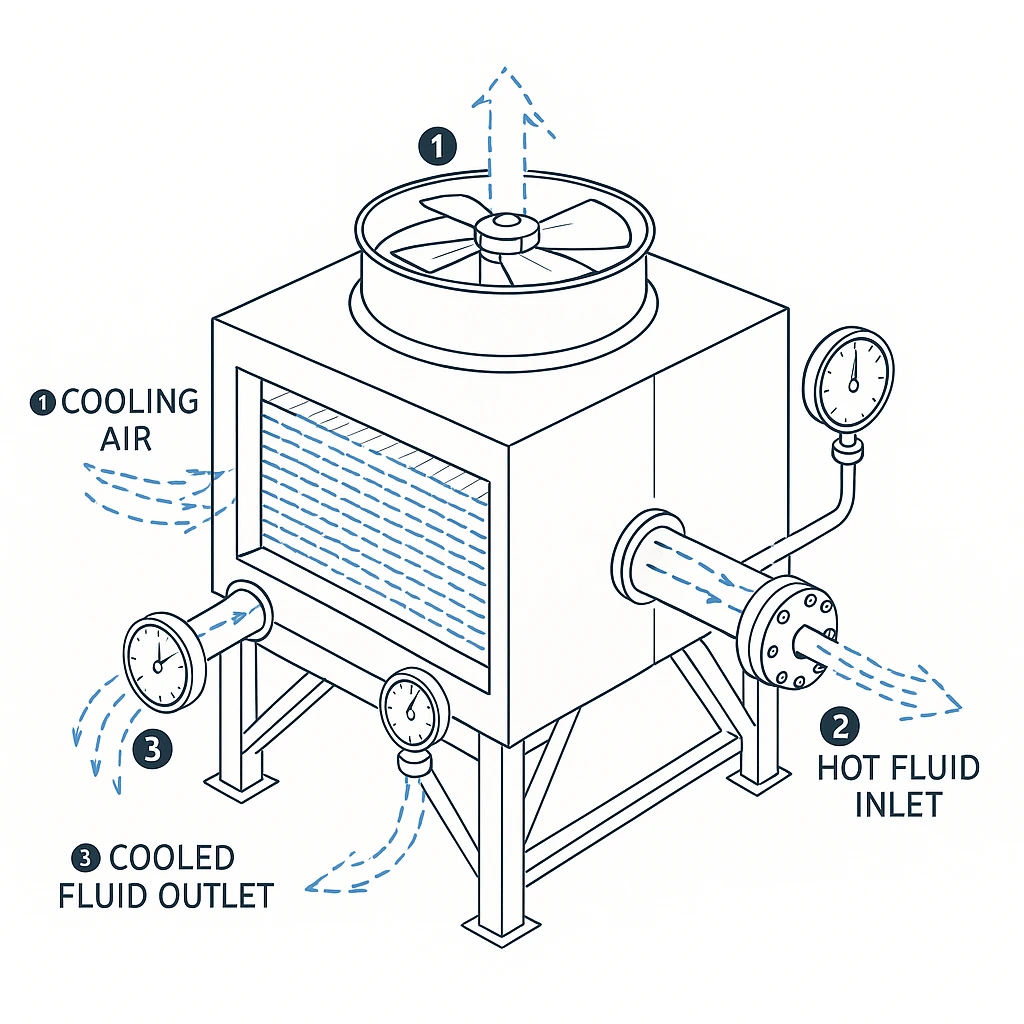
Benefits of Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
1. Water Conservation
Air-cooled heat exchangers do not require water for the cooling process, reducing the strain on water resources and eliminating the need for water treatment and disposal systems.
2. Low Maintenance and Durability
These exchangers are easy to maintain due to their simple design. With fewer components compared to water-based exchangers, they are less prone to corrosion, leaks, and fouling, making them a reliable long-term solution.
3. Versatility
Air-cooled heat exchangers are suitable for a wide range of temperatures, fluid types, and environmental conditions. They can operate efficiently even in high-temperature and arid climates, where water-based cooling solutions might not be viable.
4. Cost-Effective
Due to their low water consumption, minimal maintenance requirements, and simple installation, air-cooled heat exchangers offer a cost-effective cooling solution over the long term.
Materials and Construction
Air-cooled heat exchangers are constructed using high-quality materials that ensure durability, efficiency, and resistance to environmental factors such as heat, humidity, and corrosion. Common materials include:
- Aluminum Fins: Known for their high thermal conductivity, aluminum fins increase the heat transfer efficiency of the exchanger.
- Stainless Steel Tubes: Stainless steel is widely used for its corrosion resistance, especially in harsh industrial and marine environments.
- Carbon Steel: Used for shell construction in less demanding applications.
- Copper: Sometimes used in heat exchange coils for improved thermal conductivity.
Specifications
- Material Options: Aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, copper.
- Temperature Range: Typically between -40°C and 150°C (-40°F and 302°F), depending on the design.
- Flow Rate: From 100 liters per minute to over 10,000 liters per minute, depending on the application.
- Fan Power: Varies by model, typically ranging from 0.5 kW to 75 kW or more.
- Pressure Rating: Standard ratings from 10 bar to 40 bar.
- Size Options: Customizable to fit specific space and cooling requirements.
Why Choose Our Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers?
- High Performance: Optimized for superior heat transfer and maximum energy efficiency.
- Customizable Designs: Available in various sizes, materials, and configurations to suit different industrial and environmental needs.
- Durability: Built to withstand tough conditions and provide reliable, long-term operation.
- Eco-Friendly: Reduced water usage and environmental impact compared to traditional cooling systems.
- Cost-Effective: Low maintenance costs and no need for additional water management systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an air-cooled heat exchanger used for?
An air-cooled heat exchanger is used to transfer heat between fluids or gases and the surrounding air. It is commonly used in industries where water is unavailable or unsuitable for cooling.
2. How does an air-cooled heat exchanger work?
Air-cooled heat exchangers use fans to blow air over a series of fins or tubes, which transfer heat from the fluid inside. This air removes the heat, cooling the fluid in the process.
3. What are the advantages of air-cooled heat exchangers over water-cooled systems?
Air-cooled heat exchangers require no water source, reducing water usage and eliminating the need for water treatment systems. They are easier to maintain and are ideal for areas where water is scarce.
4. Can air-cooled heat exchangers be used in extreme temperatures?
Yes, air-cooled heat exchangers are designed to operate efficiently even in extreme temperatures, making them ideal for hot or arid environments.
5. Are air-cooled heat exchangers customizable?
Yes, they can be customized in terms of size, material, and fan power to suit the specific cooling requirements of your application.





